“8 numbers problem” in CPII 2020 Spring: solution and some related basic knowledge used in it.
Preknowledge
BFS(广度优先搜索)
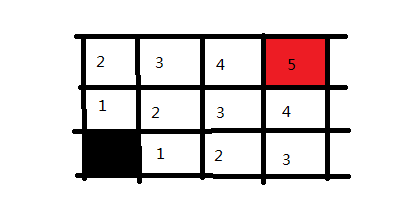
广度优先搜索较之深度优先搜索之不同在于,深度优先搜索旨在不管有多少条岔路,先一条路走到底,不成功就返回上一个路口然后就选择下一条岔路,而广度优先搜索旨在面临一个路口时,把所有的岔路口都记下来,然后选择其中一个进入,然后将它的分路情况记录下来,然后再返回来进入另外一个岔路,并重复这样的操作,用图形来表示则是这样的,例子:
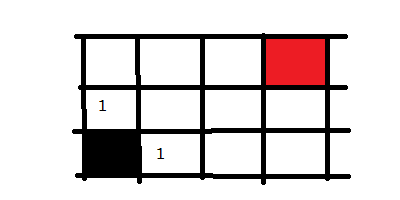
从黑色起点出发,记录所有的岔路口,并标记为走一步可以到达的。然后选择其中一个方向走进去,我们走黑点方块上面的那个,然后将这个路口可走的方向记录下来并标记为2,意味走两步可以到达的地方。
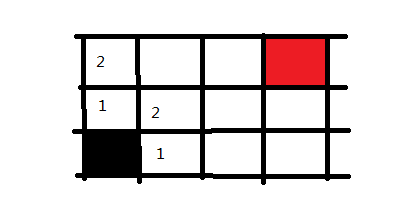
接下来,我们回到黑色方块右手边的1方块上,并将它能走的方向也记录下来,同样标记为2,因为也是走两步便可到达的地方
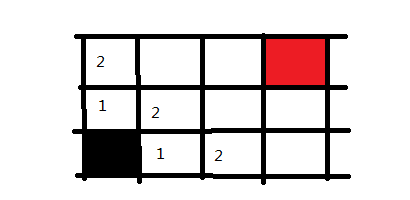
这样走一步以及走两步可以到达的地方都搜索完毕了,下面同理,我们可以迅速把三步的格子给标记出来
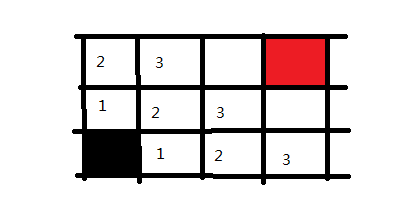
再之后是四步,五步。
我们便成功寻找到了路径,并且把所有可行的路径都求出来了。在广度优先搜索中,可以看出是逐步求解的,反复的进入与退出,将当前的所有可行解都记录下来,然后逐个去查看。在DFS中我们说关键点是递归以及回溯,在BFS中,关键点则是状态的选取和标记。
int n = 10, m = 10; //地图宽高 void BFS() { queue que; //用队列来保存路口 int graph[n][m]; //地图 int px[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}; //移动方向的数组 int py[] = {0, -1, 0, 1}; que.push(起点入队); //将起点入队 while (!que.empty()) { //只要队列不为空 auto temp = que.pop(); //得到队列中的元素 for (int i = 0; i != 4; ++i) { if(//可以走) { //标记当前格子 //将当前状态入队列,等待下次提取 } } } }注:以上两个代码只是提供思路,并非是语法正确的可运行代码。
总结
对于这两个搜索方法,其实我们是可以轻松的看出来,他们有许多差异与许多相同点的。
1.数据结构上的运用
DFS用递归的形式,用到了栈结构,先进后出。
BFS选取状态用队列的形式,先进先出。
2.复杂度
DFS的复杂度与BFS的复杂度大体一致,不同之处在于遍历的方式与对于问题的解决出发点不同,DFS适合目标明确,而BFS适合大范围的寻找。
3.思想
思想上来说这两种方法都是穷竭列举所有的情况。
From: Zhihu: Linkcheng
Cantor 展开
Target usage
Cantor 展开用于求解一个全排列的序号。例如:12345 序号为 1 ,12354 序号为 2,按字典序增加序号递增。 Cantor 逆展开用于求解序号对应的排列。
Explanation
康托展开的基本公式如下:
其中X代表该排列的排名, 代表该排列中的第i位数字在第i位其后的数字中按升序排在第几个(以0为最小)。
举个例子:在1~5的排列中,求解34152的排名。
第1位数字是3,在34152中按升序排在第2个。(最小的是第0个)故
第2位数字是4,在4152中按升序排在第2个。
第3位数字是1,在152中按升序排在第0个。
第4位数字是5,在52中按升序排在第1个。
最后一位 固定为0。
则
字典序
8 numbers problem
Content
3×3九宫棋盘,放置数码为1-8的8个棋牌,剩下一个空格,只能通过棋牌向空格的移动来改变棋盘的布局。要求:根据给定初始布局,问:至少移动几次才能从初始布局到达目标布局。
目标布局如下图:
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Input Description
3行,每行3个0-8的不重复整数,其中0表示空格所在的位置,数字间用空格隔开,表示初始布局,数据保证该初始布局一定能移到目标布局。
Output Description
一个整数,表示最少移动到目标布局的次数。
Sample
INPUT
0 7 6 8 4 3 5 2 1
OUTPUT
4
Main method
对于每种情况,可以看作 9 个数字的不同排列,也就是说会有 9!=362880 种情况,而每种情况用一个字符串进行记录,也方便调用字符串函数减少工作量。为了避免搜索重复情况,将建立一个 HASH 表。每种排列的 Cantor 展开是唯一的,故可以此作为对应关系。
每种状态的记录以及挪动元素的实现
记录
例如:将 INPUT 情况记作序列
int arr[9] = {0,7,6,8,4,3,5,2,1}
挪动元素
那么对于其中某一个元素(如 8 )向上一格,只需令 8 与它之前的第三个元素进行交换,同时需要满足:
- 之前的第三个元素是 0;
只需
arr[where_8_is_located - 3] = 0 - 不在边缘。
可以用标记该位置是否可以向左移动实现。
int mobility[9][4]={ {0,1,0,1},{0,1,1,1},{0,1,1,0},{1,1,0,1},{1,1,1,1},{1,1,1,0},{1,0,0,1},{1,0,1,1},{1,0,1,0} } //order in up, down, left and right, 0 means unable;同理,向左一格是与该元素之前的一个元素进行交换…
避免重复搜索
原 Blog 中利用 Hash 表 + Cantor 展开. 复习一下上面的公式和算法:(似乎是我自己记不住… )
其中X代表该排列的排名, 代表该排列中的第i位数字在第i位其后的数字中按升序排在第几个(以0为最小)。
int cantor(char x[],int n) // calculate the cantor function
{
int fac[]={1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320}; // values of factorial, from 0 to 8 (there is 9 numbers used in total)
int i,j,num=0,count; //num means X.
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
count=0;
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
if(x[j]<x[i]) count++;
num+=count*fac[n-1-i];
}
return num + 1;
}
Write-up
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX 400000 // all of the possible routes 9! = 362880
int hash [MAX];
char aim[10]="876543210";
char single_status [MAX][10]; // every single status. 9! in total
int cantor(char x[],int n) // calculate the cantor function
{
int fac[]={1,1,2,6,24,120,720,5040,40320}; // values of factorial, from 0 to 8 (there is 9 numbers used in total)
int i,j,num=0,count; //num means X.
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
count=0;
for(j=i+1;j<n;j++)
if(x[j]<x[i]) count++;
num+=count*fac[n-1-i];
}
return num + 1;
}
int bfs(int p, int q, int n){
int i,j=q+1,t,num;
char new_status[10]; // new status
for(i=p;i<=q;i++){
if(strcmp(single_status[i],aim)==0){
printf("%d",n);
return 0;
}
t=0;
while(single_status[i][t]!='0'){
t++;
}
if(t>2){ // 0 isn't in the first line
strcpy(new_status,single_status[i]);
new_status[t]=single_status[i][t-3];// down
new_status[t-3]=single_status[i][t];
num = cantor(new_status,9);
if(hash[num]==1){
strcpy(single_status[j],new_status);
hash[num] = 0;
j++;
}
}
if(t<6){
strcpy(new_status,single_status[i]);
new_status[t]=single_status[i][t+3];// down
new_status[t+3]=single_status[i][t];
num = cantor(new_status,9);
if(hash[num]==1){
strcpy(single_status[j],new_status);
hash[num] = 0;
j++;
}
}
if(t%3 != 0){
strcpy(new_status,single_status[i]);
new_status[t]=single_status[i][t-1];// down
new_status[t-1]=single_status[i][t];
num = cantor(new_status,9);
if(hash[num]==1){
strcpy(single_status[j],new_status);
hash[num] = 0;
j++;
}
}
if(t%3 != 2){
strcpy(new_status,single_status[i]);
new_status[t]=single_status[i][t+1];// down
new_status[t+1]=single_status[i][t];
num = cantor(new_status,9);
if (hash[num] == 1) {
strcpy(single_status[j], new_status);
hash[num] = 0;
j++;
}
}
}
bfs(q + 1, j - 1, n + 1);
return 0;
}
int main(){
int i,trans;
for(i = 0;i<9;i++){
scanf("%d",&trans);
single_status[0][i]=trans+'0';
}
single_status[0][9]='\0';
for(i = 0;i<MAX;i++){
hash[i]=1;
}
hash[cantor(single_status[0],9)]=0;
bfs(0,0,0);
return 0;
}